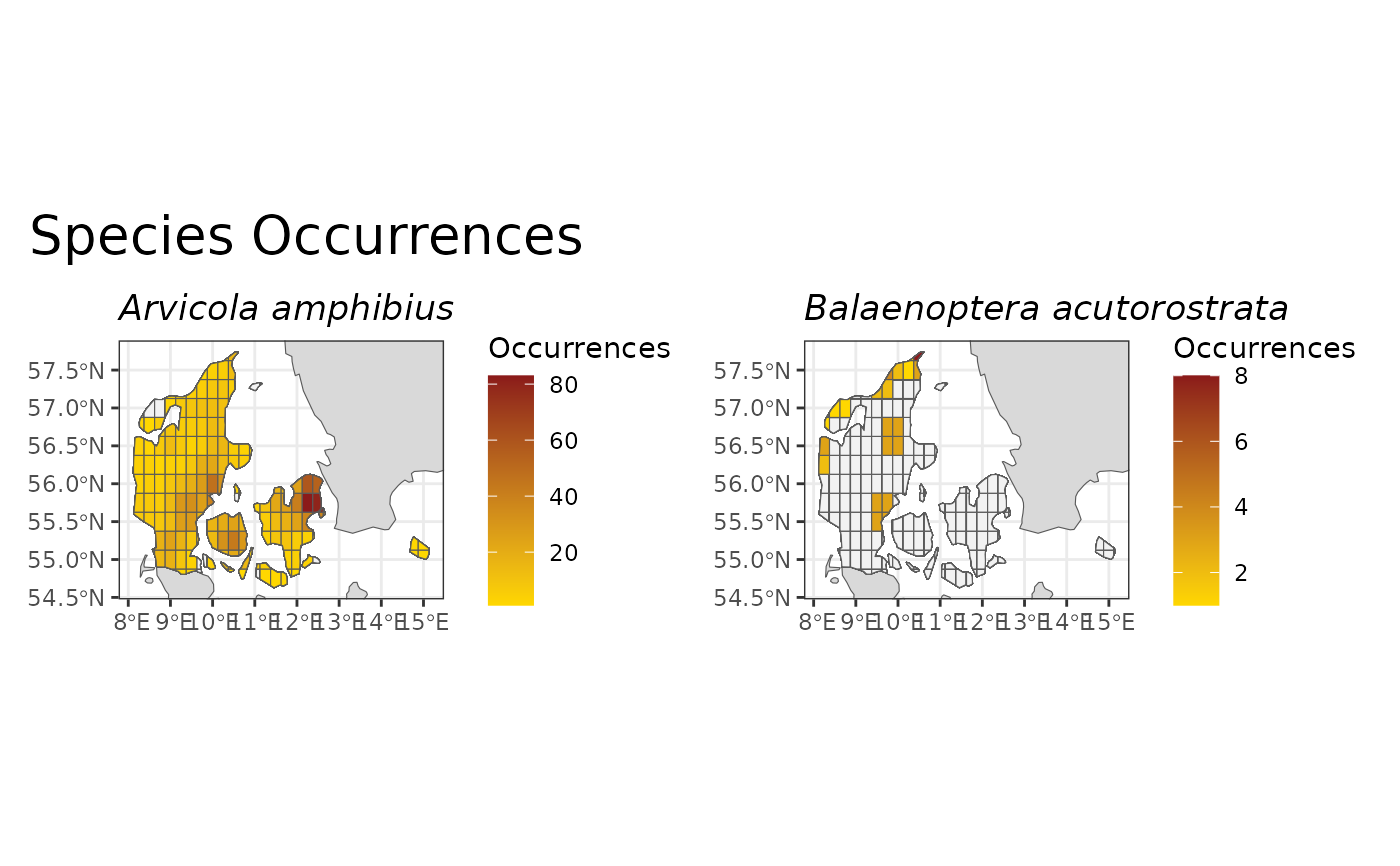
This function calculates the number of occurrences for individual species over a gridded map or as a time series (see 'Details' for more information).
Arguments
- data
A data cube object (class 'processed_cube').
- ...
Arguments passed on to
compute_indicator_workflowci_type(Optional) Type of bootstrap confidence intervals to calculate. (Default: "norm"). Select "none" to avoid calculating bootstrap CIs.
cell_size(Optional) Length of grid cell sides, in km or degrees. If set to "grid" (default), this will use the existing grid size of your cube. If set to "auto", this will be automatically determined according to the geographical level selected. This is 100 km or 1 degree for 'continent' or 'world', 10 km or (for a degree-based CRS) the native resolution of the cube for 'country', 'sovereignty' or 'geounit'. If level is set to 'cube', cell size will be the native resolution of the cube for a degree-based CRS, or for a km-based CRS, the cell size will be determined by the area of the cube: 100 km for cubes larger than 1 million sq km, 10 km for cubes between 10 thousand and 1 million sq km, 1 km for cubes between 100 and 10 thousand sq km, and 0.1 km for cubes smaller than 100 sq km. Alternatively, the user can manually select the grid cell size (in km or degrees). Note that the cell size must be a whole number multiple of the cube's resolution.
level(Optional) Spatial level: 'cube', 'continent', 'country', 'world', 'sovereignty', or 'geounit'. (Default: 'cube')
region(Optional) The region of interest (e.g., "Europe"). This parameter is ignored if level is set to 'cube' or 'world'. (Default: NULL)
ne_type(Optional) The type of Natural Earth data to download: 'countries', 'map_units', 'sovereignty', or 'tiny_countries'. This parameter is ignored if level is set to 'cube' or 'world'. (Default: "countries")
ne_scale(Optional) The scale of Natural Earth data to download: 'small' - 110m, 'medium' - 50m, or 'large' - 10m. (Default: "medium")
output_crs(Optional) The CRS you want for your calculated indicator. (Leave blank to let the function choose a default based on grid reference system.)
first_year(Optional) Exclude data before this year. (Uses all data in the cube by default.)
last_year(Optional) Exclude data after this year. (Uses all data in the cube by default.)
spherical_geometry(Optional) If set to FALSE, will temporarily disable spherical geometry while the function runs. Should only be used to solve specific issues. (Default is TRUE).
make_valid(Optional) Calls st_make_valid() from the sf package after creating the grid. Increases processing time but may help if you are getting polygon errors. (Default is FALSE).
num_bootstrap(Optional) Set the number of bootstraps to calculate for generating confidence intervals. (Default: 100)
shapefile_path(optional) Path of an external shapefile to merge into the workflow. For example, if you want to calculate your indicator particular features such as protected areas or wetlands.
shapefile_crs(Optional) CRS of a .wkt shapefile. If your shapefile is .wkt and you do NOT use this parameter, the CRS will be assumed to be EPSG:4326 and the coordinates will be read in as lat/long. If your shape is NOT a .wkt the CRS will be determined automatically.
invert(optional) Calculate an indicator over the inverse of the shapefile (e.g. if you have a protected areas shapefile this would calculate an indicator over all non protected areas within your cube). Default is FALSE.
include_land(Optional) Include occurrences which fall within the land area. Default is TRUE. *Note that this purely a geographic filter, and does not filter based on whether the occurrence is actually terrestrial. Grid cells which fall partially on land and partially on ocean will be included even if include_land is FALSE. To exclude terrestrial and/or freshwater taxa, you must manually filter your data cube before calculating your indicator.
include_ocean(Optional) Include occurrences which fall outside the land area. Default is TRUE. Set as "buffered_coast" to include a set buffer size around the land area rather than the entire ocean area. *Note that this is purely a geographic filter, and does not filter based on whether the occurrence is actually marine. Grid cells which fall partially on land and partially on ocean will be included even if include_ocean is FALSE. To exclude marine taxa, you must manually filter your data cube before calculating your indicator.
buffer_dist_km(Optional) The distance to buffer around the land if include_ocean is set to "buffered_coast". Default is 50 km.
force_grid(Optional) Forces the calculation of a grid even if this would not normally be part of the pipeline, e.g. for time series. This setting is required for the calculation of rarity or Hill diversity, and is forced on by indicators that require it. (Default: FALSE)
Value
An S3 object with the classes 'indicator_map' or 'indicator_ts' and 'spec_occ' containing the calculated indicator values and metadata.
Details
Species occurrences are considered an essential biodiversity variable (EBV). They are mapped by calculating the total number of occurrences of a given species for each cell. This represents the occurrence frequency distribution, and also indicates the observed species distribution. The number of occurrences can act as a proxy for relative abundance of species with a similar detectability, which is an important aspect of biodiversity although not an indicator when calculated in isolation.
Examples
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
so_map <- spec_occ_map(example_cube_1, level = "country",
region = "Denmark", include_ocean = FALSE)
plot(so_map, c(2440728, 4265185))
} # }
so_ts <- spec_occ_ts(example_cube_1, first_year = 1985)
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 2 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 2 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 22 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 48 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 3 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
#> [1] "All values of t are equal to 1 \n Cannot calculate confidence intervals"
plot(so_ts, c(2435767, 2434793))