Create spatial pattern within a polygon
Source:R/create_spatial_pattern.R
create_spatial_pattern.RdThis function creates a raster with a spatial pattern for the area of a polygon.
Usage
create_spatial_pattern(
polygon,
resolution,
spatial_pattern = c("random", "clustered"),
seed = NA,
n_sim = 1
)Arguments
- polygon
An sf object with POLYGON geometry.
- resolution
A numeric value defining the resolution of the raster cells.
- spatial_pattern
Specifies the desired spatial pattern. It can be a character string (
"random"or"clustered") or a numeric value ≥ 1 (1 means random distribution, larger values indicate more clustering). The default is"random"."clustered"corresponds to a value of 10. See Details.- seed
A positive numeric value setting the seed for random number generation to ensure reproducibility. If
NA(default), thenset.seed()is not called at all. If notNA, then the random number generator state is reset (to the state before calling this function) upon exiting this function.- n_sim
Number of simulations. Each simulation is a different layer in the raster. Default is 1.
Value
An object of class SpatRaster with a spatial pattern for the area of
the given polygon with n_sim layers sampling_p'n_sim' containing the
sampling probabilities from the raster grid for each simulation.
Details
The spatial_pattern argument changes the range parameter of the
spherical variogram model. spatial_pattern = 1 means the range has the same
size as the grid cell, which is defined in the resolution argument. The
function gstat::vgm() is used to implement the spherical variogram model.
See also
gstat::vgm() and its range argument
Other occurrence:
sample_occurrences_from_raster(),
simulate_random_walk(),
simulate_timeseries()
Examples
# Load packages
library(sf)
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyterra)
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘tidyterra’
#> The following object is masked from ‘package:stats’:
#>
#> filter
# Create polygon
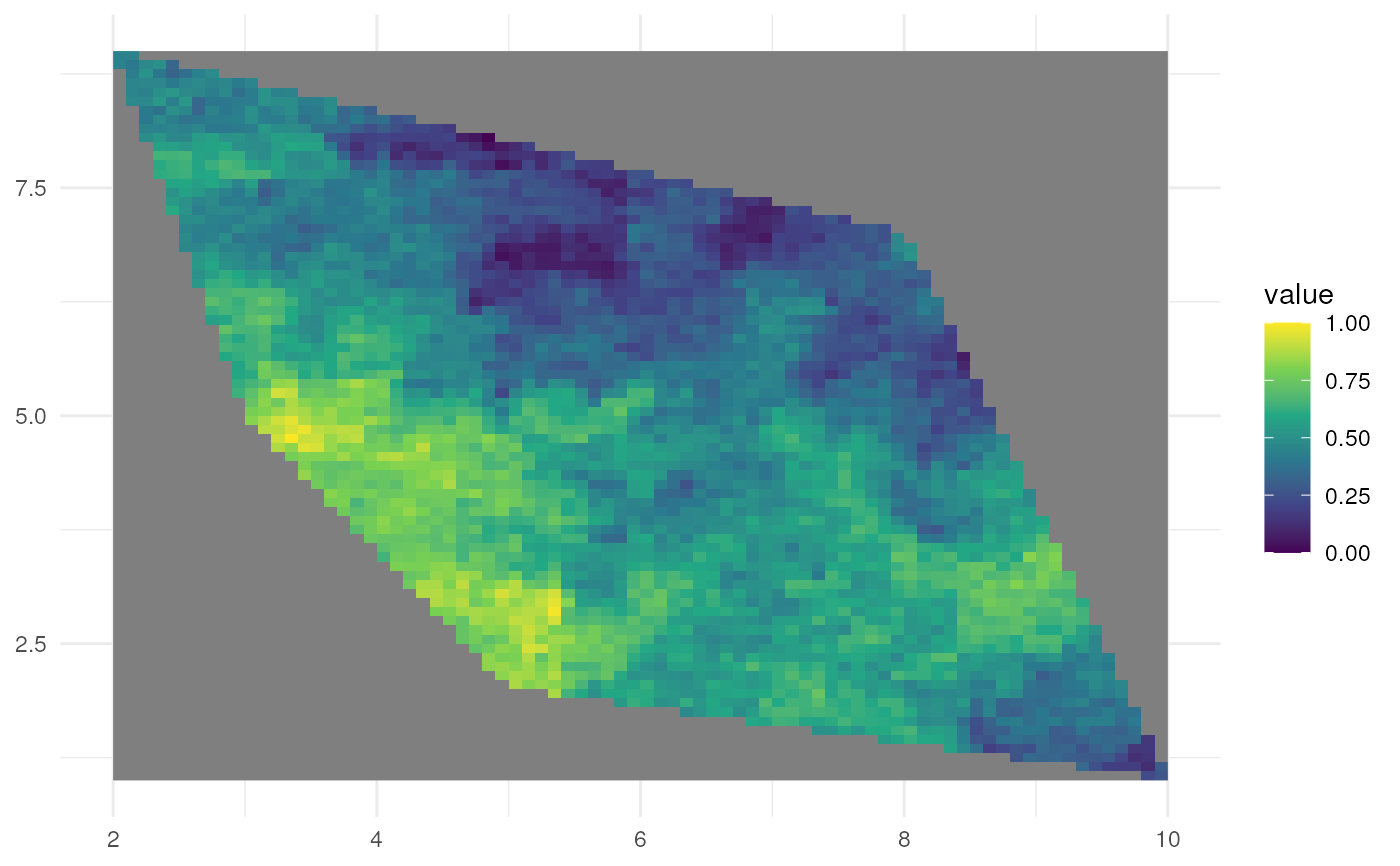
plgn <- st_polygon(list(cbind(c(5, 10, 8, 2, 3, 5), c(2, 1, 7, 9, 5, 2))))
# 1. Random spatial pattern
rs_pattern_random <- create_spatial_pattern(
polygon = plgn,
resolution = 0.1,
spatial_pattern = "random",
seed = 123)
#> [using unconditional Gaussian simulation]
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rs_pattern_random) +
scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") +
theme_minimal()
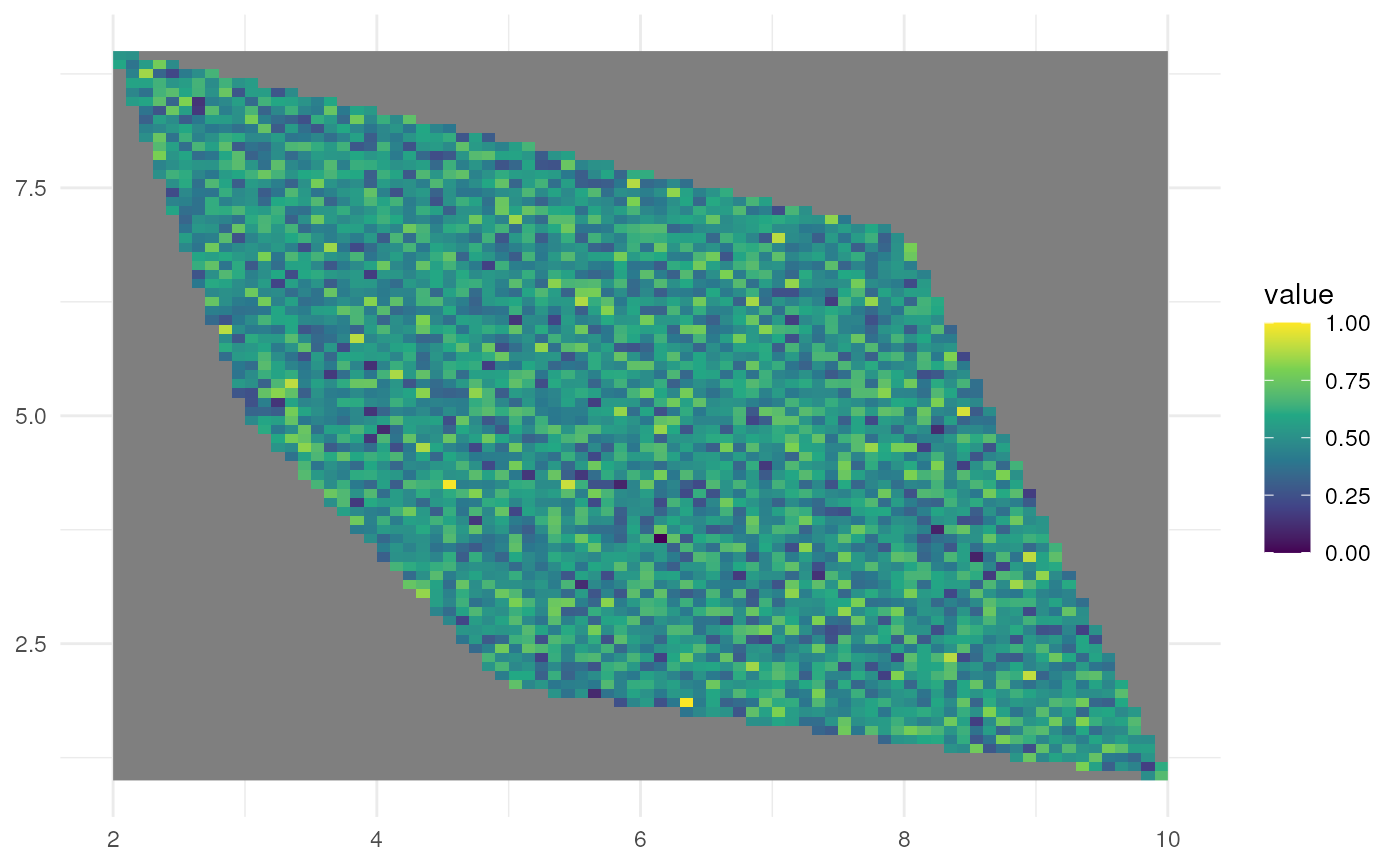 # 2. Clustered spatial pattern
rs_pattern_clustered <- create_spatial_pattern(
polygon = plgn,
resolution = 0.1,
spatial_pattern = "clustered",
seed = 123)
#> [using unconditional Gaussian simulation]
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rs_pattern_clustered) +
scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") +
theme_minimal()
# 2. Clustered spatial pattern
rs_pattern_clustered <- create_spatial_pattern(
polygon = plgn,
resolution = 0.1,
spatial_pattern = "clustered",
seed = 123)
#> [using unconditional Gaussian simulation]
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rs_pattern_clustered) +
scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") +
theme_minimal()
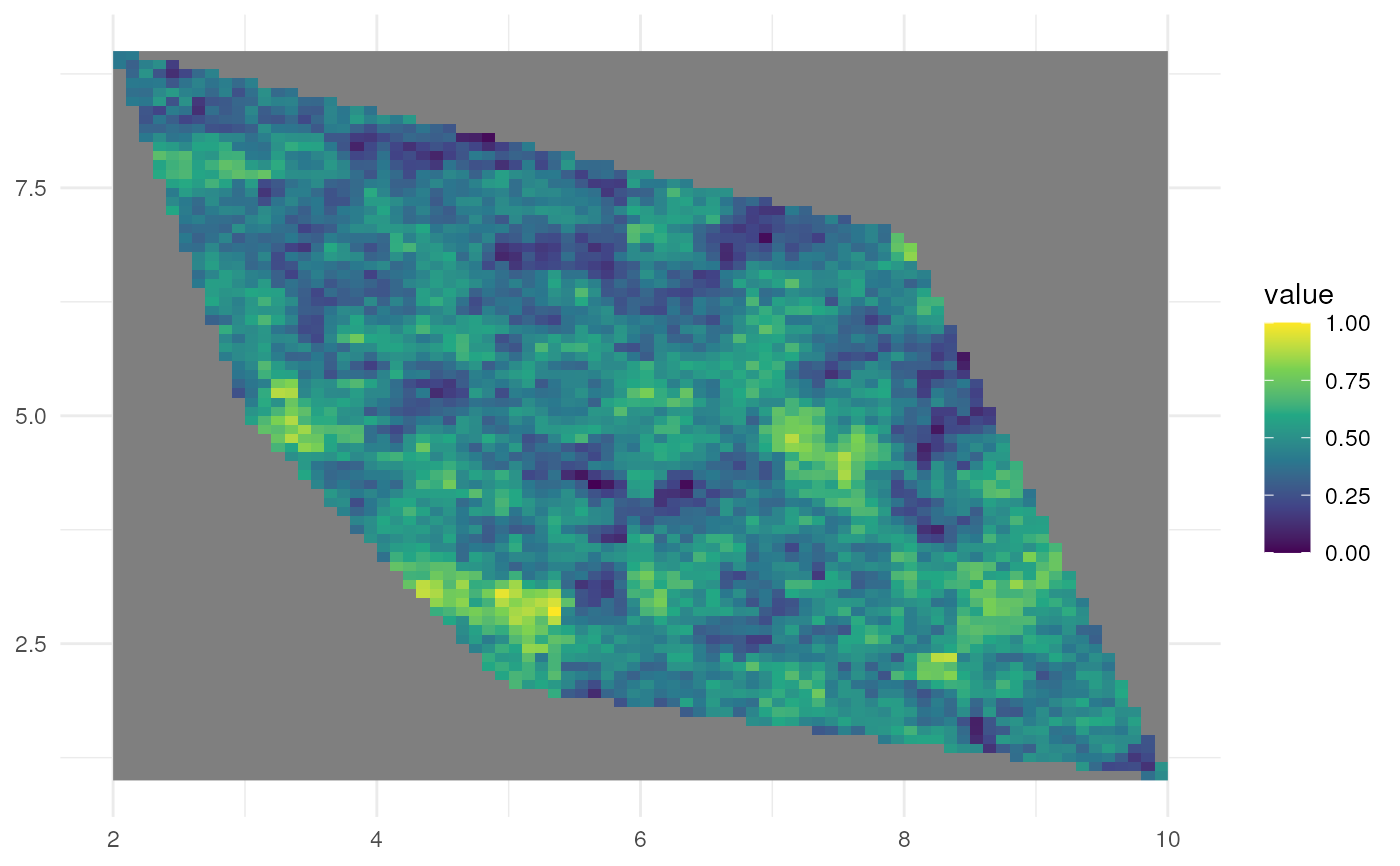 # 3. User defined spatial pattern
# Large scale clustering
rs_pattern_large <- create_spatial_pattern(
polygon = plgn,
resolution = 0.1,
spatial_pattern = 100,
seed = 123)
#> [using unconditional Gaussian simulation]
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rs_pattern_large) +
scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") +
theme_minimal()
# 3. User defined spatial pattern
# Large scale clustering
rs_pattern_large <- create_spatial_pattern(
polygon = plgn,
resolution = 0.1,
spatial_pattern = 100,
seed = 123)
#> [using unconditional Gaussian simulation]
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rs_pattern_large) +
scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") +
theme_minimal()